Vitamin B12 Deficiency
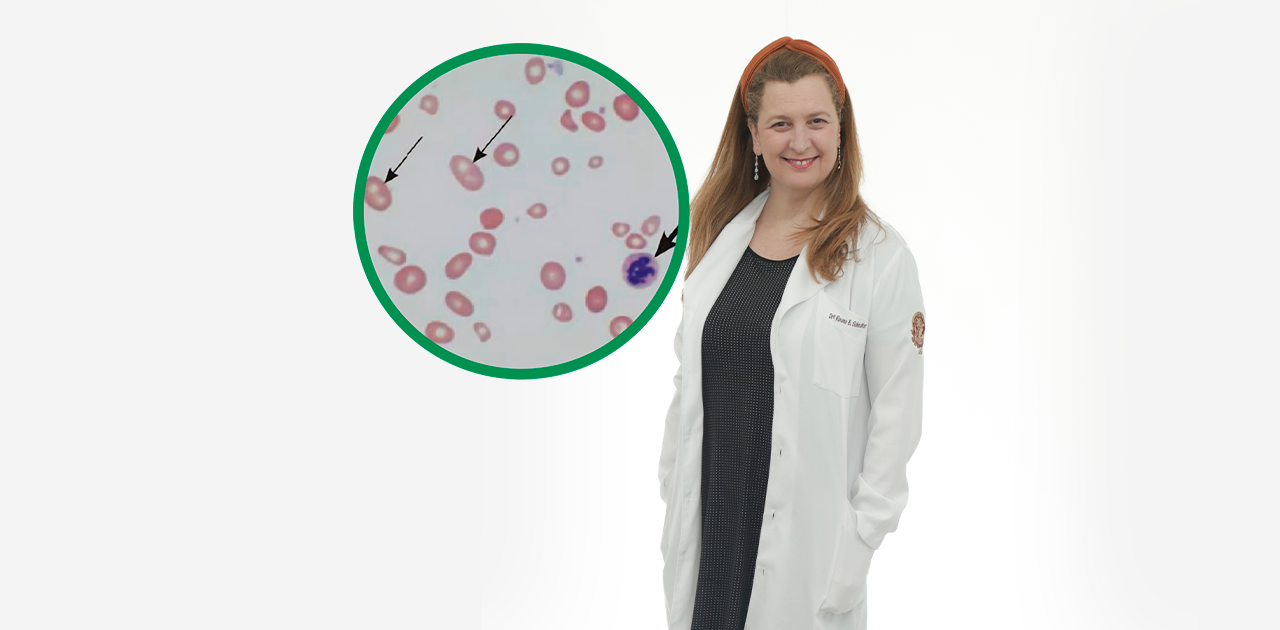
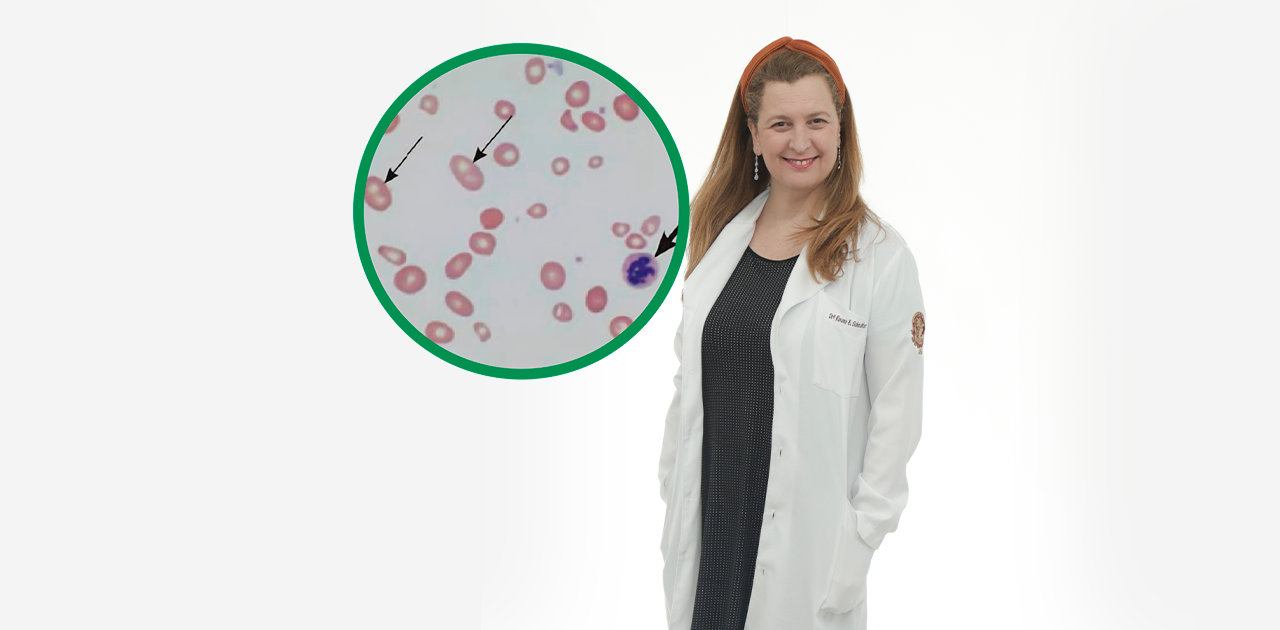
Dra. Rosana Schechter is a gastroenterologist in Israel, specializing in digestive diseases and digestive motility. Vitamin B12 deficiency is a condition that can lead to neurological and hematological problems, such as fatigue, weakness, memory loss, and anemia. It occurs when there is insufficient intake or absorption of this essential vitamin.
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can occur due to various factors related to the consumption, absorption, and storage of this essential vitamin. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and determining the most effective treatment.
Inadequate Consumption
Inadequate consumption of foods rich in vitamin B12, such as meats, eggs, and dairy products, can lead to a deficiency. This is more common in people who follow restrictive diets, such as vegans and vegetarians, who do not consume animal sources of this vitamin. In such cases, supplementation may be recommended to prevent deficiency.
Inadequate Absorption
Even with adequate vitamin B12 intake, gastrointestinal issues can impair absorption. Disorders such as Celiac Disease, Crohn’s Disease, Pernicious Anemia, Autoimmune Gastritis, or even after bariatric surgeries can cause this. In such cases, treatment should focus on correcting the factors affecting absorption.
Inadequate Storage
The human body stores vitamin B12 in the liver, and inadequate storage may occur in situations of poor nutrition or metabolic disorders. In cases of insufficient storage, deficiency may manifest more quickly, even with adequate intake. Medical evaluation helps identify these cases and adjust treatment accordingly.
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can manifest in various ways, primarily affecting the nervous and hematologic systems. Common symptoms include extreme fatigue, weakness, difficulty concentrating, and memory loss. Additionally, neurological symptoms such as tingling and numbness in the extremities, a feeling of “loss of balance,” and mood changes like irritability and depression may occur.
Diagnosis of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
The diagnosis of vitamin B12 deficiency is made through blood tests that assess vitamin B12 levels in the body. The analysis may be supplemented with tests to check other parameters, such as homocysteine and methylmalonic acid, which are indicative of deficiency. The doctor also considers clinical symptoms and the patient’s dietary history for an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Treatment for vitamin B12 deficiency varies based on severity and underlying causes. In mild cases, oral supplementation with tablets or capsules may be sufficient. For more severe deficiencies or when intestinal absorption is compromised, vitamin B12 injections are often necessary. Additionally, including B12-rich foods such as meats and dairy products is recommended for long-term maintenance.
Prevention of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Preventing vitamin B12 deficiency involves a balanced diet with B12-rich foods like meats, fish, and eggs. For vegans and vegetarians, it is essential to include fortified foods or use supplementation. Regular monitoring, especially in high-risk groups like the elderly and those with intestinal problems, is also crucial to avoid deficiency and ensure optimal B12 levels in the body.
What are the benefits and functions of vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 plays several essential roles in the body, being crucial for red blood cell formation and the proper functioning of the nervous system. It helps in DNA synthesis and the formation of myelin, the substance that covers nerve fibers, allowing efficient conduction of nerve impulses. Additionally, B12 is important for energy metabolism, contributing to the conversion of food into usable energy by the body.
What are the main sources of this vitamin?
Vitamin B12 is mainly found in animal-derived foods. The main sources include red meats, fish, seafood, eggs, and dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt. For people following vegetarian or vegan diets, supplementation or consumption of B12-fortified foods, such as cereals and plant-based milks, becomes essential to prevent deficiency.
What causes low vitamin B12 levels?
Low vitamin B12 levels in the body can occur due to various factors. Insufficient intake of B12-rich foods is one of the main causes, especially in people following vegetarian or vegan diets without proper supplementation. Additionally, absorption issues in the gastrointestinal tract, such as in intestinal diseases or after gastric surgeries, can also hinder vitamin absorption. Other conditions, such as aging and the use of medications that interfere with gastric acid production, can contribute to the deficiency.
What are the consequences of low vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 deficiency can have several serious consequences for health, especially in the nervous and hematologic systems. The main complications include megaloblastic anemia, which causes fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath, and neurological issues, such as tingling, memory loss, and coordination difficulties. In severe and untreated cases, prolonged B12 deficiency can lead to permanent nerve damage and cognitive impairment. It can also increase the risk of heart diseases and psychiatric disorders like depression and psychosis.
How to replenish vitamin B12 when it is low?
Vitamin B12 replenishment depends on the severity of the deficiency and the underlying cause. In mild cases, oral supplementation may be sufficient to restore levels in the body. However, in more severe deficiencies or when absorption is compromised, B12 injections are necessary to ensure the vitamin is rapidly absorbed by the body. In cases of chronic absorption problems, continuous replenishment may be required, along with dietary adjustments to include B12-rich foods.
Precautions during vitamin B12 supplementation
During the vitamin B12 supplementation process, it is important to follow medical guidelines regarding the correct dosage to avoid excess. Medical monitoring is essential to track B12 levels in the blood and adjust the dosage as needed. In some cases, supplementation may cause side effects such as diarrhea or allergic reactions, which should be closely monitored. Additionally, it is crucial to ensure that the treatment addresses the underlying cause of the deficiency, whether due to poor diet, gastric disorders, or other factors.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a condition that can severely impact health if not diagnosed and treated appropriately. Its effects range from symptoms such as fatigue and memory loss to more serious complications, such as permanent neurological damage. Fortunately, with early diagnosis and proper replenishment, it is possible to treat the deficiency and prevent complications. Dr. Rosana offers specialized follow-up care, both in Israel and through teleconsultations, to ensure that each patient receives appropriate treatment, promoting long-term health and well-being.
Schedule your appointment with Dr. Rosana Schechter.
Gastroenterologist in Israel, specialist in digestive motility and digestive diseases.
Dr. Rosana offers in-clinic consultations, home visits in selected regions of Israel, and teleconsultations for patients anywhere in Brazil and around the world.
If you are looking for a reliable diagnosis, personalized treatment, or wish to obtain a second medical opinion from an experienced specialist, contact us today.
Frequently Asked Questions – Vitamin B12 Deficiency
What happens when someone has low vitamin B12?
B12 deficiency can cause extreme fatigue, tingling, memory loss, concentration difficulties, and even mood changes. In more severe cases, it can affect the nervous system and proper red blood cell production, leading to megaloblastic anemia.
How to raise vitamin B12 quickly?
Rapid replenishment is usually done with supplements in capsules, sublingual tablets, or injections, depending on the severity of the deficiency and the patient’s absorption capability. Only a doctor can recommend the correct method after evaluating the tests.
What is the best medicine to replenish vitamin B12?
There is no one “best” medicine, but rather the most suitable for each patient. In some cases, oral supplementation is enough; in others, intramuscular injections are necessary. The choice depends on the vitamin level, the presence of associated diseases, and intestinal absorption.
What to eat to increase vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is found mainly in animal-derived foods: red meat, chicken, fish, eggs, milk, and dairy products. For vegetarians or vegans, supplementation is usually essential.
Which fruit is richest in vitamin B12?
No fruit contains significant amounts of vitamin B12. B12 is found only in animal-derived foods or specific supplements.
What is the best vitamin B12 to take?
The most commonly used forms are cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin. Both are effective, but the choice depends on medical indication, the patient’s profile, and the method of administration.
What is the best type of vitamin B12 to take?
For mild deficiencies, oral supplementation may be sufficient. In cases of poor intestinal absorption or severe deficiency, injectable replenishment is recommended. The decision should be individualized after medical evaluation.
Which vitamin is good for physical and mental fatigue?
In addition to vitamin B12, other B vitamins, iron, vitamin D, and folic acid can influence physical and mental well-being. However, only laboratory tests can indicate exactly which nutrients are lacking.
How can I treat a Vitamin B12 Deficiency with Dr. Rosana?
Dr. Rosana Schechter offers comprehensive care to investigate and treat vitamin B12 deficiency:
- In-person consultations in Israel, with clinical evaluation and test requests.
- Home care in Israel, bringing medical care to the patient.
- Teleconsultations across Brazil, providing diagnosis, guidance for replenishment, and follow-up remotely.
- Second medical opinions, assisting patients who already have a previous diagnosis or ongoing treatments and seek more security.
Other Articles
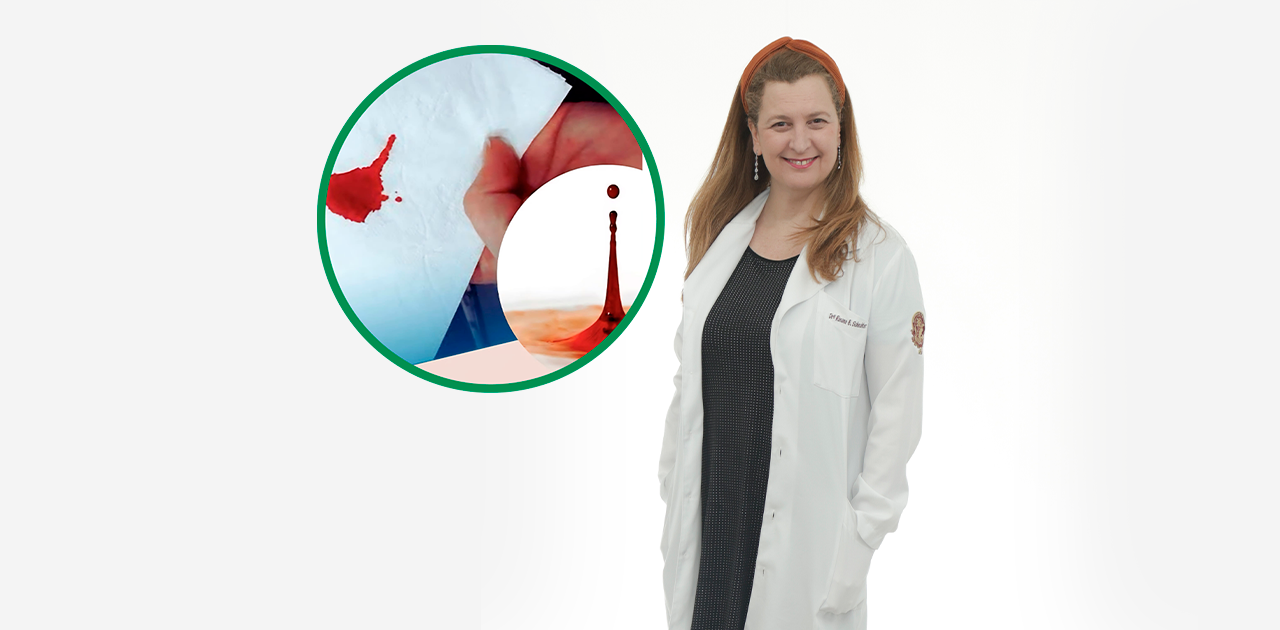

Occult blood in stool can indicate serious gastrointestinal diseases. Dr. Rosana investigates and treats with precision and care.
Elevated liver enzymes can indicate liver problems. Dr. Rosana investigates the causes and provides appropriate, individualized treatment.
Iron deficiency can cause fatigue and anemia. Dr. Rosana Schechter investigates causes and offers safe, individualized treatment.
Where am I?
EliteMed Specialist Clinic
Haret Street 12,
Building B, 5th floor
Modi'in Macabim Reut
(Ayala 360 complex)
Tel: 073-321-4181
Online consultation
+972 55-775-9259
Service hours:
Sunday to Thursday
from 6:00 AM to 5:00 PM
(Brasília time)
8:00 AM to 8:00 PM
(Tel Aviv time)
Follow me on social media
Contact me
Main Diagnoses
- Hiatal Hernia
- Gastroesophageal Reflux
- Reflux Esophagitis
- Achalasia
- Gastric Ulcer
- Duodenal Ulcer
- Helicobacter pylori
- Fatty Liver Disease
- Gallstones
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Crohn’s Disease
- Retocolite Ulcerativa
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Diverticulosis
- Diverticulitis
- Intestinal Polyps
- Colorectal Cancer
- Hemorrhoids





