Iron Deficiency
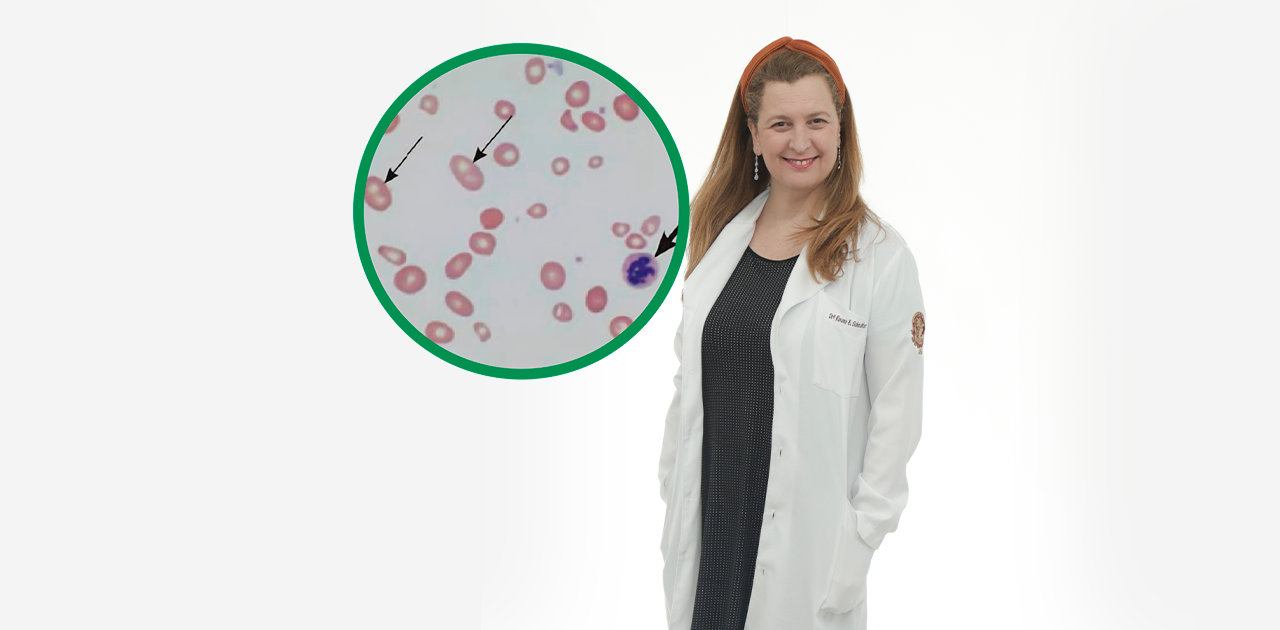
Dra. Rosana Schechter is a gastroenterologist in Israel, specializing in digestive diseases and digestive motility. Iron deficiency is one of the most common nutritional imbalances and can lead to anemia if left untreated. Common causes include inadequate diets, blood loss, or intestinal absorption issues.
Causes of Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency can occur due to insufficient intake of the mineral through the diet, chronic blood loss, such as from ulcers, heavy menstruation, or gastrointestinal bleeding, as well as difficulties in intestinal absorption. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for determining the correct treatment.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency
Common symptoms include persistent fatigue, weakness, dizziness, hair loss, brittle nails, and pallor. In more advanced cases, palpitations, shortness of breath, and difficulty concentrating may arise. These signs should be investigated to prevent the progression to anemia.
Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency
Diagnosis is made through blood tests that assess hemoglobin, ferritin, serum iron, and other hematimetric indices. In some cases, additional tests are needed to investigate possible hidden bleeding or absorption issues in the gastrointestinal tract.
Main Clinical Signs of Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency can manifest in different ways in the body, often subtly. Recognizing its clinical signs is crucial to avoid complications, as the lack of this mineral affects tissue oxygenation and overall health. Below are the main symptoms that deserve attention.
Pallor
Iron deficiency reduces hemoglobin production, compromising tissue oxygenation. As a result, the skin may appear pale, especially on the face, gums, and ocular mucosa. This is one of the most visible signs and should be observed carefully during a clinical exam.
Constant Fatigue and Exhaustion
Persistent fatigue is one of the most common symptoms of iron deficiency. Without sufficient iron, the body produces less energy, and the patient feels constantly drained, even after rest. This condition significantly affects productivity and quality of life.
Shortness of Breath
With a reduced capacity to carry oxygen in the blood, simple activities like climbing stairs or walking may cause shortness of breath. This symptom is more frequent in cases of iron deficiency associated with anemia, when hemoglobin levels are already very low.
Feeling Cold
Iron deficiency can affect the body’s thermal regulation. As a result, the patient may feel cold frequently, even in environments with comfortable temperatures. This symptom, when associated with other clinical signs, may indicate the need for laboratory investigation.
Cravings for Ice or Non-Nutritive Substances
A characteristic symptom of iron deficiency is pica, a condition where a person feels the urge to eat non-nutritive substances like ice, dirt, or paper. This behavior indicates the severity of the deficiency and should be discussed with a doctor as soon as possible.
Brittle Nails and Hair Loss
Iron deficiency affects the health of tissues and skin appendages. Therefore, it is common to notice weak nails that break easily and excessive hair loss. These signs may be confused with aesthetic problems but often have a nutritional origin.
How Iron Deficiency Affects Women’s Health
Iron deficiency is common among women of reproductive age and can impact energy levels, immunity, and overall quality of life. Understanding the main factors and what constitutes adequate iron levels is essential for preventing complications and maintaining balanced health.
Menstrual Cycle is the Main Factor
The menstrual cycle, especially when marked by heavy or prolonged bleeding, is one of the major causes of iron deficiency in women. The recurrent loss of blood reduces the mineral reserves in the body, increasing the risk of developing anemia if proper replenishment is not provided.
Treatment of Iron Deficiency
Treatment for iron deficiency depends on the identified cause. In many cases, it involves dietary adjustments, with increased consumption of meats, dark leafy vegetables, and legumes, in addition to oral supplementation prescribed by a doctor. When there are absorption difficulties or significant blood losses, intravenous iron replenishment may be necessary. Specialized follow-up ensures safety in management and prevention of relapses.
Conclusion
Iron deficiency is a common condition, but it can have a significant impact on health if not identified and treated early. Recognizing the symptoms, conducting the appropriate tests, and seeking specialized medical care make all the difference in ensuring an accurate diagnosis and improving quality of life.
Schedule your appointment with Dr. Rosana Schechter.
Gastroenterologist in Israel, specialist in digestive motility and digestive diseases.
Dr. Rosana offers in-clinic consultations, home visits in selected regions of Israel, and teleconsultations for patients anywhere in Brazil and around the world.
If you are looking for a reliable diagnosis, personalized treatment, or wish to obtain a second medical opinion from an experienced specialist, contact us today.
Frequently Asked Questions – Iron Deficiency
What can iron deficiency cause?
Iron deficiency reduces hemoglobin production, which hinders oxygen transport in the blood. This can lead to fatigue, pallor, hair loss, brittle nails, dizziness, palpitations, and weakened immunity. In more severe cases, it progresses to iron-deficiency anemia.
How to replenish iron in the body quickly?
Rapid replenishment can be done with oral supplements or, in specific cases, with intravenous iron. The choice depends on the degree of deficiency, the patient’s tolerance to medications, and clinical need. Medical monitoring is essential to avoid excess iron, which can also be harmful.
Can you have iron deficiency without anemia?
Yes. Often, iron deficiency begins silently, when ferritin (iron reserves) is low but hemoglobin is still normal. In these cases, symptoms like fatigue, weakness, and decreased physical performance may arise, even without a formal anemia diagnosis.
Can you have iron deficiency without anemia?
Yes. Often, iron deficiency begins silently, when ferritin (iron reserves) is low but hemoglobin is still normal. In these cases, symptoms like fatigue, weakness, and decreased physical performance may arise, even without a formal anemia diagnosis.
What are the symptoms of low ferritin?
Low ferritin reflects reduced iron stores. The most common symptoms include chronic fatigue, hair loss, brittle nails, pallor, frequent headaches, and, in some cases, increased susceptibility to infections.
How can I treat Iron Deficiency with Dr. Rosana?
Dr. Rosana Schechter provides comprehensive care for patients with iron deficiency in different formats:
- In-person consultation in Israel, with a full evaluation and specific test requests.
- Home care services in Israel, bringing medical care to your residence.
- Teleconsultation across Brazil, offering detailed diagnosis, guidance for replenishment, and continuous follow-up at a distance.
- Second medical opinions, assisting in clarifying doubts and reviewing recommendations from other healthcare professionals.
Other Articles
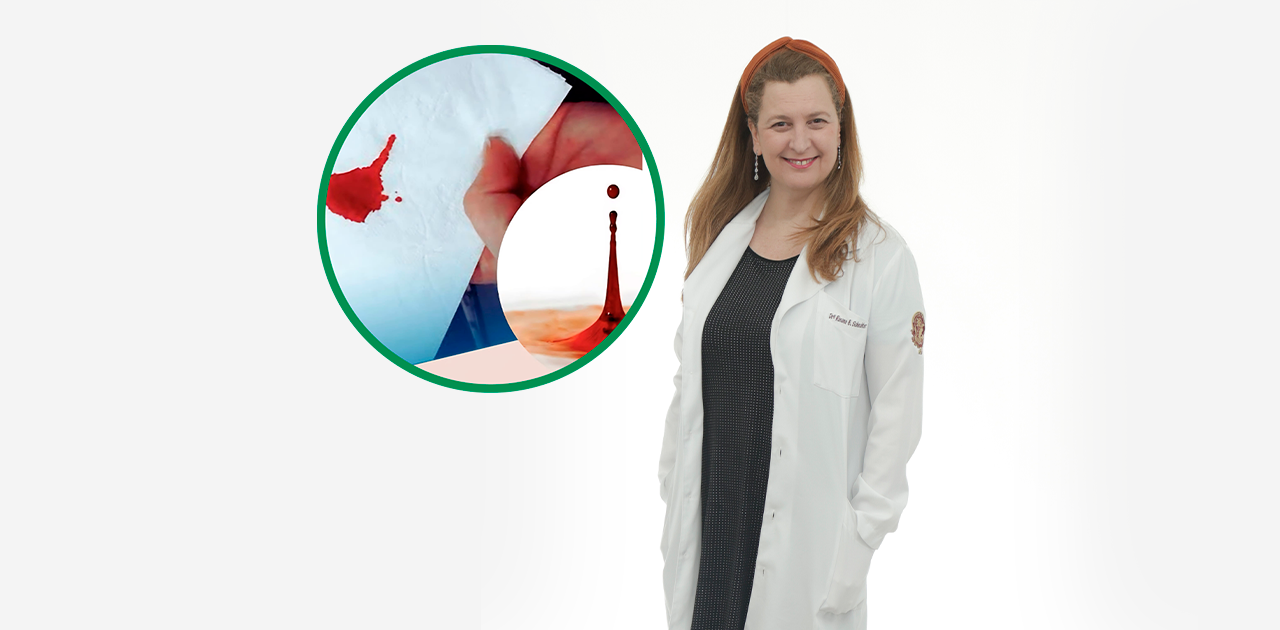

Occult blood in stool can indicate serious gastrointestinal diseases. Dr. Rosana investigates and treats with precision and care.
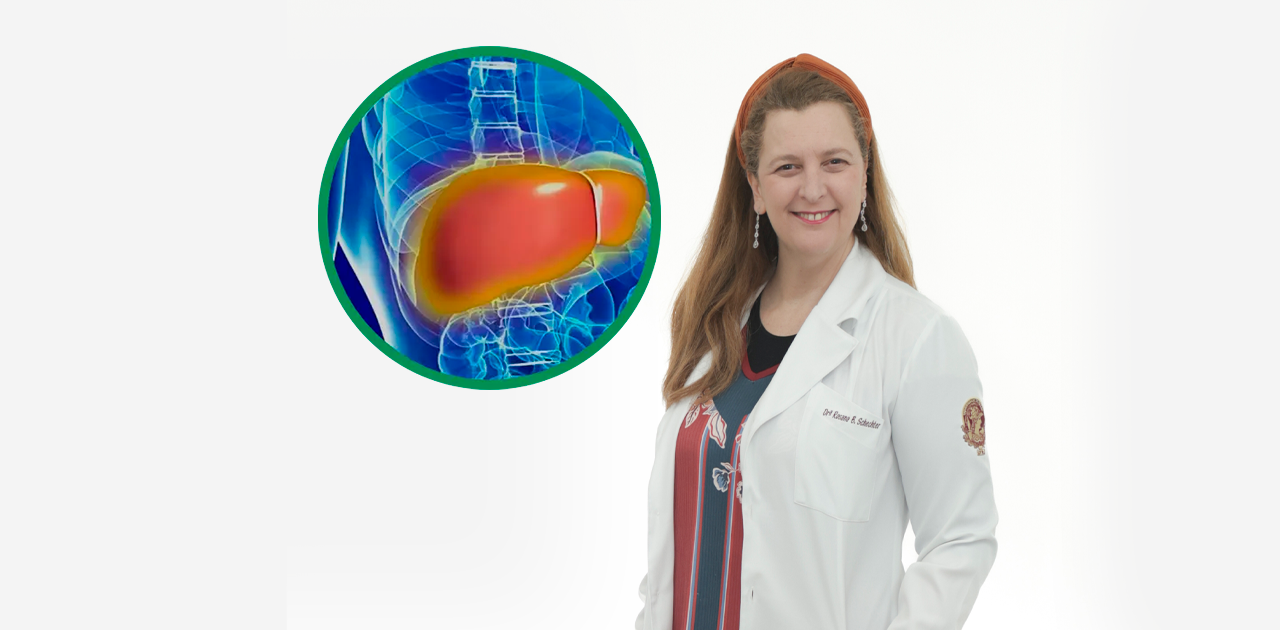
Elevated liver enzymes can indicate liver problems. Dr. Rosana investigates the causes and provides appropriate, individualized treatment.

Iron deficiency can cause fatigue and anemia. Dr. Rosana Schechter investigates causes and offers safe, individualized treatment.
Where am I?
EliteMed Specialist Clinic
Haret Street 12,
Building B, 5th floor
Modi'in Macabim Reut
(Ayala 360 complex)
Tel: 073-321-4181
Online consultation
+972 55-775-9259
Service hours:
Sunday to Thursday
from 6:00 AM to 5:00 PM
(Brasília time)
8:00 AM to 8:00 PM
(Tel Aviv time)
Follow me on social media
Contact me
Main Diagnoses
- Hiatal Hernia
- Gastroesophageal Reflux
- Reflux Esophagitis
- Achalasia
- Gastric Ulcer
- Duodenal Ulcer
- Helicobacter pylori
- Fatty Liver Disease
- Gallstones
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Crohn’s Disease
- Retocolite Ulcerativa
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Diverticulosis
- Diverticulitis
- Intestinal Polyps
- Colorectal Cancer
- Hemorrhoids





