Hiatal Hernia – Treatment in Israel
A Dra. Rosana Schechter is a gastroenterologist in Israel, specializing in digestive diseases and digestive motility. With extensive experience, she provides accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment for hiatal hernia, offering in-person and home care consultations in Israel, as well as teleconsultations for patients throughout Brazil.
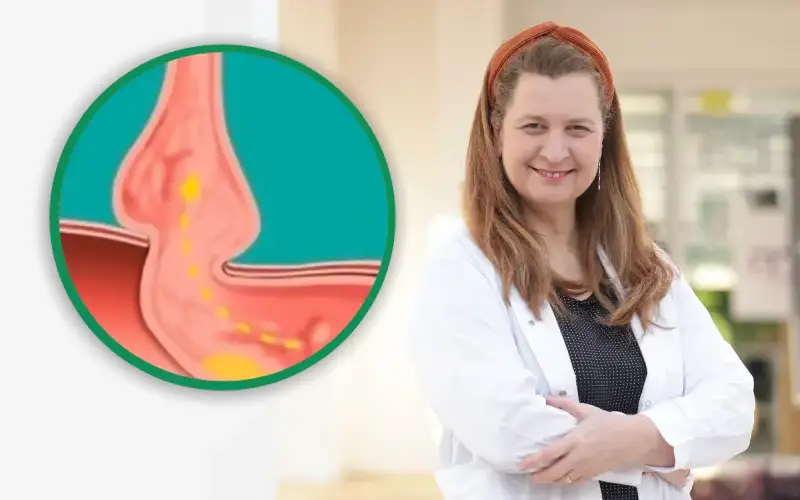
What is a hiatal hernia?
Diagnosis and Types of Hiatal Hernia
Hiatal hernia can be classified into two main types:
Sliding hiatal hernia: This is the most common form and occurs when the esophagus and part of the stomach slide up into the chest.
Paraesophageal hernia: Less common but more serious, it occurs when only the stomach protrudes alongside the esophagus, potentially causing complications.
Identifying the type of hernia is essential to determine the best treatment plan. As a gastroenterologist in Israel, Dr. Rosana Schechter conducts a thorough evaluation, focusing on accurate diagnosis and an individualized approach.
What are the treatments for hiatal hernia?
The treatment of hiatal hernia depends on the severity of symptoms and the type of hernia. In mild cases, Dr. Rosana Schechter, a specialist in digestive motility, usually recommends lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medications to reduce stomach acidity. In more advanced cases or when there is a risk of complications, surgery may be indicated.
What are the symptoms of hiatal hernia?
The most common symptoms of hiatal hernia include:
• Heartburn and burning sensation in the chest
• Feeling of acid reflux
• Frequent belching
• Abdominal or chest pain
• Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
• Chronic cough or hoarseness
These symptoms are often mistaken for other digestive conditions. Therefore, it is essential to consult an experienced gastroenterologist for an accurate diagnosis.
How is the diagnosis made?
Gastroenterologist Dr. Rosana Schechter uses modern and specific tests to confirm the presence of a hiatal hernia, such as:
• Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
• Contrast X-ray of the esophagus and stomach
• Esophageal manometry (a test that evaluates digestive motility)
• Esophageal pH monitoring (measures acid reflux)
The choice of tests is personalized according to each patient.
Treatment for hiatal hernia
Treatment may involve:
• Weight management
• Avoiding fatty foods, caffeine, and alcoholic beverages
• Sleeping with the head of the bed elevated
• Use of medications such as proton pump inhibitors
• Surgical treatment (in refractory cases)”
What kind of doctor should I see?
If you experience symptoms of reflux, frequent heartburn, or suspect a hiatal hernia, you should consult a gastroenterologist, especially a specialist in digestive diseases and digestive motility.
Dr. Rosana Schechter is a gastroenterologist in Israel with over 20 years of experience and a solid academic background in Brazil. Her care focuses on early diagnosis, effective treatment, and a humanized approach to follow-up.
Schedule your appointment with Dr. Rosana Schechter.
Gastroenterologist in Israel, specialist in digestive motility and digestive diseases.
Dr. Rosana offers in-clinic consultations, home visits in selected regions of Israel, and teleconsultations for patients anywhere in Brazil and around the world.
If you are looking for a reliable diagnosis, personalized treatment, or wish to obtain a second medical opinion from an experienced specialist, contact us today.
Frequently Asked Questions – Hiatal Hernia
What is good for treating hiatal hernia?
A hiatal hernia does not resolve on its own, but its symptoms can be managed with dietary changes, weight control, elevating the head of the bed, medications, and, in some cases, surgery. Dr. Rosana Schechter, a gastroenterologist in Israel, offers personalized treatments with a focus on digestive motility and patient well-being.
What should you not eat with a hiatal hernia?
Patients with hiatal hernia should avoid fatty foods, fried foods, chocolate, coffee, alcoholic beverages, and soft drinks. These items can promote acid reflux, worsening symptoms. Gastroenterologist Dr. Rosana Schechter recommends a balanced diet focused on reducing digestive discomfort and esophageal inflammation.
What can make a hiatal hernia worse?
Factors such as obesity, large meals, lying down immediately after eating, smoking, and stress increase abdominal pressure, worsening a hiatal hernia. Dr. Rosana Schechter, a specialist in digestive diseases, focuses on prevention, patient education, and an individualized approach to control the progression of the condition.
What happens to the stomach in someone with a hiatal hernia?
In individuals with a hiatal hernia, part of the stomach moves up into the chest through the diaphragm. This compromises the function of the valve that prevents reflux, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, pain, and a burning sensation. Gastroenterologist Dr. Rosana Schechter, experienced in digestive motility, performs tests to accurately assess the stomach’s anatomy and function.
Can someone with a hiatal hernia take omeprazole?
Yes, omeprazole is often prescribed to reduce stomach acidity in patients with a hiatal hernia. However, its use should be supervised by a gastroenterologist. Dr. Rosana Schechter evaluates each case to recommend the most appropriate medication and, if necessary, adjusts it over time based on symptoms and test results.
What causes a hiatal hernia to grow?
Increased intra-abdominal pressure due to obesity, chronic cough, constipation, pregnancy, or heavy lifting can contribute to the growth of a hiatal hernia. Gastroenterologist Dr. Rosana Schechter in Israel provides preventive guidance and ongoing follow-up to reduce the risk of progression.
What should someone with a hiatal hernia eat for breakfast?
Patients with hiatal hernia should avoid fatty foods, fried foods, chocolate, coffee, alcoholic beverages, and soft drinks. These items can promote acid reflux, worsening symptoms. Gastroenterologist Dr. Rosana Schechter recommends a balanced diet focused on reducing digestive discomfort and esophageal inflammation.
Can a hiatal hernia burst?
No. A hiatal hernia does not ‘burst,’ but it can increase in size and, in rare cases, cause complications such as strangulation or obstruction. Therefore, follow-up with an experienced gastroenterologist, such as Dr. Rosana Schechter, is essential to safely monitor and manage the condition.
Where can I have a consultation for hiatal hernia treatment in Israel?
You can have a consultation with Dr. Rosana Schechter, a gastroenterologist in Israel, at the We Care Clinic in Modiin-Maccabim-Reut. She also conducts home visits in selected areas and provides teleconsultations. With extensive experience in digestive diseases, she offers personalized diagnosis and treatment.
Does Dr. Rosana treat hiatal hernia via teleconsultation?
Yes, Dr. Rosana Schechter, a specialist in digestive motility, provides teleconsultations for patients in Brazil, Israel, or anywhere in the world. Through video consultations, she evaluates symptoms and test results, and can even offer a second medical opinion, assisting in the diagnosis and treatment of hiatal hernia with expertise and empathy.
Other Articles
Dificuldade de Engolir (Disfagia)
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo. Perguntas Frequentes Os procedimentos estéticos da Ello

Hiatal Hernia – Treatment in Israel
Gastroenterologist in Israel, Dr. Rosana Schechter treats hiatal hernia with a focus on digestive motility and an individualized approach.
Where am I?
EliteMed Specialist Clinic
EliteMed Specialist Clinic Haret Street 12, Building B, 5th floor Modi'in Macabim Reut (Ayala 360 complex) Tel: 073-321-4181
Teleconsultation
+972 55-775-9259
Service hours:
Sunday to Thursday, from 6:00 AM to 5:00 PM (Brasília time) 8:00 AM to 8:00 PM (Tel Aviv time)
Follow me on social media
Contact me
Main Diagnoses
- Hiatal Hernia
- Gastroesophageal Reflux
- Reflux Esophagitis
- Achalasia
- Gastric Ulcer
- Duodenal Ulcer
- Helicobacter pylori
- Fatty Liver Disease
- Gallstones
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Crohn’s Disease
- Retocolite Ulcerativa
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Diverticulosis
- Diverticulitis
- Intestinal Polyps
- Colorectal Cancer
- Hemorrhoids





